What Is Epithelioid Mesothelioma?
Epithelioid mesothelioma is one of the three cell types of malignant mesothelioma. The other cell types are sarcomatoid and biphasic.
Over 50% of patients diagnosed with mesothelioma have the epithelioid cell type, according to the American Cancer Society (ACS).
Specially trained doctors called pathologists can identify epithelial mesothelioma cells by reviewing biopsy samples under a microscope.
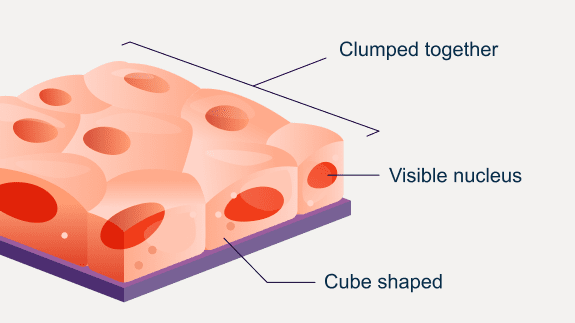
Epithelioid mesothelioma cells are identified by their:
- Clearly visible nucleus
- Slower movement
- Square, cube, long, or flat shape
- Tendency to stick together
Epithelioid patients generally have a better prognosis than patients with other mesothelioma cell types. This is because epithelioid tumors spread (metastasize) slower and are easier to treat.
Get our Free Mesothelioma Guide to learn more about this cell type and what treatment options are available.
What Causes Epithelioid Mesothelioma Cancer?
Asbestos exposure causes epithelioid mesothelioma.
When asbestos-containing products are disturbed or damaged, tiny fibers can be released into the air. When you breathe in or swallow these fibers, they can settle in the lining of the lungs or abdomen, leading to scarring and inflammation.
Over 10 to 50 years, this irritation can damage healthy epithelial cells, eventually leading to mesothelioma cancer.
Asbestos was used in various industries in the U.S. military up until the early 1980s, so many people with mesothelioma today are veterans and retired blue-collar workers.
“Asbestos was a critical material for World War II. It was used in insulation on the ships. It was used in gaskets, brake linings. That’s when my dad first started working, and that’s when he was first exposed.”
– Patricia, daughter of a veteran diagnosed with mesothelioma
Malignant Epithelioid Mesothelioma Symptoms
The symptoms of epithelioid mesothelioma depend on where the cancer is located in the body.
For example, cancer in the lining around the lungs (pleura) causes different symptoms than cancer in the abdominal lining (peritoneum).
| Symptoms of Pleural Epithelioid Mesothelioma | Symptoms of Peritoneal Epithelioid Mesothelioma |
|---|---|
| Chest pain | Abdominal pain |
| Fatigue | Constipation or diarrhea |
| Fluid buildup in the chest (pleural effusion) | Fluid buildup in the abdomen (peritoneal ascites) |
| Shortness of breath | Night sweats |
| Worsening cough | Unexplainable weight loss |
These symptoms usually get worse as the cancer spreads, so it’s important to see a specialist right away if you notice them. Contact our Patient Advocates so we can help you find a mesothelioma doctor in your area.
Epithelioid mesothelioma is the most common of three mesothelioma cell types, and it's also the easiest to treat since it doesn't spread as quickly. View Transcript.
Duration: 1 min 27 sec
Mesothelioma, a form of cancer that can develop in the lining of the lungs heart or abdomen has different cell types. Today we’ll shed some light on epithelioid mesothelioma, the most common cell type, about 70% of mesothelioma patients have the epithelioid or epithelial cell type. These patients have a distinct advantage when it comes to treatment options. Epithelial cells tend to grow relatively slowly allowing for more effective treatment strategies such as surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. Thanks to this slower growth pattern, patients diagnosed with epithelioid mesothelioma have a better prognosis and higher survival rates compared to the other two cell types which are sarcomatoid and basic. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with mesothelioma, it’s crucial to consult with a doctor who specializes in this rare cancer. They can provide you with the most up-to-date information on treatment options and guide you through your journey toward better health. Remember, early detection and Ely intervention are key to improving outcomes for mesothelioma patients. Stay informed, seek support, and explore all available resources to ensure the best possible care and support for yourself or your loved one. Remember, you are not alone in this fight. Help is just to call away. Contact us today to be connected with a patient advocate who can recommend doctors and treatments for epithelioid mesothelioma.
How Is Epithelial Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
Your doctor will use a series of imaging scans and tests to confirm an epithelioid mesothelioma diagnosis. Learn more about how mesothelioma is diagnosed below.
1. Physical Examination
The symptoms of epithelial mesothelioma can be vague, so they’re often mistaken for bronchitis, pneumonia, or digestive problems. A physical exam is a good first step to help your doctor rule out these more common conditions.
During the exam, your doctor will review your medical history and check your vital signs. They’ll use a stethoscope to listen to your breathing and check for signs of fluid buildup, which is an early sign of malignant pleural mesothelioma — the most common type of this cancer.
Your doctor might also check for any lumps or unusual masses around your chest and abdomen.
2. Imaging Scans
If your doctor sees or hears anything unusual during your physical exam, they can use imaging scans to look for tumors, nodules, scar tissue, or other signs of disease.
These may include:
- Computed tomography (CT) scans
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans
- Positron emission tomography (PET) scans
- X-rays
Imaging tests are a key part of an epithelial mesothelioma diagnosis since they show details your doctor wouldn’t be able to see in a physical exam.
3. Blood Tests for Biomarkers
Some mesothelioma doctors may order blood tests as part of an epithelioid mesothelioma diagnosis. Certain blood tests can show biomarkers (indicators) associated with asbestos exposure.
For example, the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) recommends a specific biomarker test called immunohistochemistry staining. This test helps doctors identify certain proteins, such as calretinin, that are key indicators of mesothelioma.
4. Fluid or Tissue Biopsy
If imaging scans or blood tests show signs of cancer, your doctor will order a biopsy. A biopsy is the only way to confirm if you have epithelial mesothelioma.
After numbing the area with an anesthetic, your doctor will collect a small fluid or tissue sample through a tiny needle. You may feel some pressure during the procedure, which is normal.
A pathologist will then look at the sample under a microscope to see if it contains mesothelioma cells and identify the cell type (epithelioid, sarcomatoid, or biphasic).
Talking to your doctor about mesothelioma can be overwhelming. Download our Free Checklist of Questions to Ask Your Doctor and get the clarity you need to understand your health and next steps.
Epithelioid Mesothelioma Subtypes
There are several subtypes of epithelioid mesothelioma that can be harder to treat. Most of these cell subtypes are rare and affect a very small number of patients.
- Adenomatoid: This subtype makes up roughly 6% of epithelioid pleural mesothelioma cases.
- Cystic: The cystic cell subtype is typically benign (not cancerous) and found in women with peritoneal mesothelioma.
- Deciduoid: This cell subtype is diagnosed in 5% of mesothelioma patients.
- Lymphohistiocytoid: Only a few lymphohistiocytoid mesothelioma cases have ever been reported (less than 1%).
- Small-cell: This extremely rare subtype is often mistaken for other small-cell cancers.
- Solid: This subtype forms in patterns that look like sheets or nests and has an average prognosis of just over 1 year.
- Tubulopapillary: Patients with these cube-shaped cells have an average prognosis of almost 2 years.
- Well-differentiated papillary: Papillary mesothelioma cells are more common in women than men and do not spread quickly.
Your doctor can check your biopsy results to see if you have one of these epithelial subtypes and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Epithelioid Mesothelioma Life Expectancy and Prognosis
The average life expectancy for epithelioid mesothelioma is nearly 2 years with surgery. Compared to the other two cell types, epithelial mesothelioma has a better health outlook since it’s less aggressive and responds better to treatments.
| Mesothelioma Cell Type | Median Survival With Surgery |
|---|---|
| Epithelioid | 22.2 months |
| Sarcomatoid | 12.4 months |
| Biphasic | 6.4 months |
Epithelial patients who get surgery after radiation therapy have an average prognosis of 36 months, according to a study published in Communications Biology.


“When it comes to mesothelioma, the epithelioid type tends to have a better outlook than other cell types. That means there’s more reason to stay positive and hopeful about treatment possibilities.”
What Is the Epithelial Mesothelioma Survival Rate?
Survival rate is the percentage of people who are still alive a certain number of years after a mesothelioma diagnosis.
The table below provides overall survival rates for epithelioid mesothelioma with different treatment options.
| Treatment Type | 2-Year Survival Rate | 5-Year Survival Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Surgery | 45% | 14% |
| Chemotherapy | 35% | 9% |
| Radiotherapy | 40% | 12% |
| Immunotherapy | 37% | 7% |
| Surgery and Chemotherapy | 45% | 15% |
These survival rates show how treatments have worked for others, but everyone’s situation is different. Your age, cancer stage, and other factors can affect your epithelioid mesothelioma prognosis. While survival rates provide helpful insights, they don’t define your future.
Get our Free Mesothelioma Guide shipped overnight to learn more about improving your prognosis and life expectancy.
Epithelial Mesothelioma Treatment Options
Treatment for epithelioid mesothelioma typically includes options like surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and radiation. Many patients benefit from multimodal therapy, which combines two or more different treatments to target the cancer.
Some of these treatments can also serve as palliative care to reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
Surgery
Mesothelioma patients with the epithelioid cell type are more likely to qualify for surgery than those with sarcomatoid or biphasic cells.
Surgeries for epithelial mesothelioma include:
- Cytoreduction with heated chemotherapy for peritoneal mesothelioma
- Extrapleural pneumonectomy (EPP) for pleural mesothelioma
- Pleurectomy with decortication (P/D) for pleural mesothelioma
In a recent study, P/D surgery was more effective than EPP surgery for pleural epithelioid mesothelioma. Patients who got a P/D lived over 2.5 years, and patients who underwent an EPP lived just 1.5 years.


“Typically for epithelioid mesothelioma, we offer surgery up front, followed by adjuvant chemotherapy or immunotherapy.”
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses cancer-fighting drugs to shrink mesothelioma tumors and kill cancer cells.
The most common chemotherapy regimen for epithelioid mesothelioma is pemetrexed with cisplatin or carboplatin.
Most patients receive multiple rounds of mesothelioma chemotherapy with a few weeks off between treatments so they can recover.
Immunotherapy
Mesothelioma immunotherapy helps the body’s immune system better identify and attack cancer cells.
Three immunotherapy drugs are approved to treat epithelioid mesothelioma:
Other immunotherapy drugs are being tested in clinical trials to see if they can help epithelioid mesothelioma patients live longer.
According to a recent case study, one patient went into complete remission from epithelioid peritoneal mesothelioma with Keytruda and chemotherapy.
This means all signs and symptoms of his cancer disappeared. The patient is still in remission more than 4 years later.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses powerful high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells by damaging their DNA.
Doctors often recommend this treatment to shrink tumors before surgery or to manage symptoms if the cancer is unresectable (inoperable).
Get our Free Mesothelioma Guide to learn more about the latest treatments that could improve your prognosis and quality of life.
Emerging Treatments in Clinical Trials
New and innovative treatments for epithelioid mesothelioma are being tested in clinical trials. These emerging treatments could potentially help patients live longer with fewer symptoms.
Some of these emerging treatments include:
- Gene therapy: Adds specific genes to epithelial mesothelioma cells to make them more responsive to cancer treatments.
- Mesothelioma vaccines: Boost the immune system by teaching it to find and attack cancer cells.
- Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC): Delivers chemotherapy as a spray directly to the abdomen.
- Targeted therapy: Uses drugs to attack cancerous epithelial mesothelioma cells directly while leaving healthy cells alone.
Your doctor can help determine if a clinical trial is right for you. Our Patient Advocates are also available to guide you through the process.
Find Epithelioid Mesothelioma Treatment
If you’ve been diagnosed with epitheloid mesothelioma, having the right medical team by your side is crucial for your treatment and recovery.
Mesothelioma Hope can help make the process of starting treatment as straightforward and easy as possible. Our dedicated team is here to guide you every step of the way, from connecting you with the right specialist to preparing you for your first appointment.
Call us today at (866) 608-8933 or get our Free Mesothelioma Guide shipped overnight to learn more about how we can help.
Mesothelioma Epithelioid Type FAQs
What is the cause of epithelioid mesothelioma?
Exposure to asbestos is the only known cause of epithelioid mesothelioma.
When you breathe in or swallow asbestos fibers, they can get stuck in the lining of the lungs, abdomen, or heart, causing inflammation. This can damage healthy cells and cause mesothelioma cancer to develop after 10 to 50 years.
What are the stages of epithelioid mesothelioma?
There are four epithelioid mesothelioma stages:
- Stage 1: The tumor is small and hasn’t spread to lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
- Stage 2: The tumor is larger or has spread to nearby lymph nodes but hasn’t spread to other areas of the body.
- Stage 3: The cancer is more advanced, with a larger tumor and possible spread to nearby tissues or multiple lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: Cancer has spread to other parts of the body (metastasis).
These stages help doctors understand how far the cancer has progressed and what types of treatment are best for each patient.
What is the survival rate for epithelioid mesothelioma?
The survival rate for epithelioid mesothelioma varies depending on the stage of the disease, the overall health of the patient, and the specific treatments used.
- With chemotherapy, 35% of patients survive 2 years, and 9% survive over 5 years.
- With immunotherapy and chemotherapy, 37% of patients survive 2 years, and 7% survive over 5 years.
- With chemotherapy and surgery, 45% of patients survive 2 years, and 15% survive over 5 years.
Is epithelioid mesothelioma curable?
While epithelioid mesothelioma is a serious and challenging cancer, multimodal therapy may help slow it down or stop it from spreading. Some patients have even achieved remission from epithelial mesothelioma, meaning their cancer is no longer detectable.
The key to surviving mesothelioma is starting treatment with a specialist as early as possible. Contact our team today to connect with the best mesothelioma doctors near you.







